[SQL] SQL과 NoSQL의 차이
in Development on DataBase, Sql, Nosql
![[SQL] SQL과 NoSQL의 차이](/assets/img/development/database/2022-12-29/sql_vs_nosql_cover.png)
#목차
SQL(Structured Query Language) 이란?
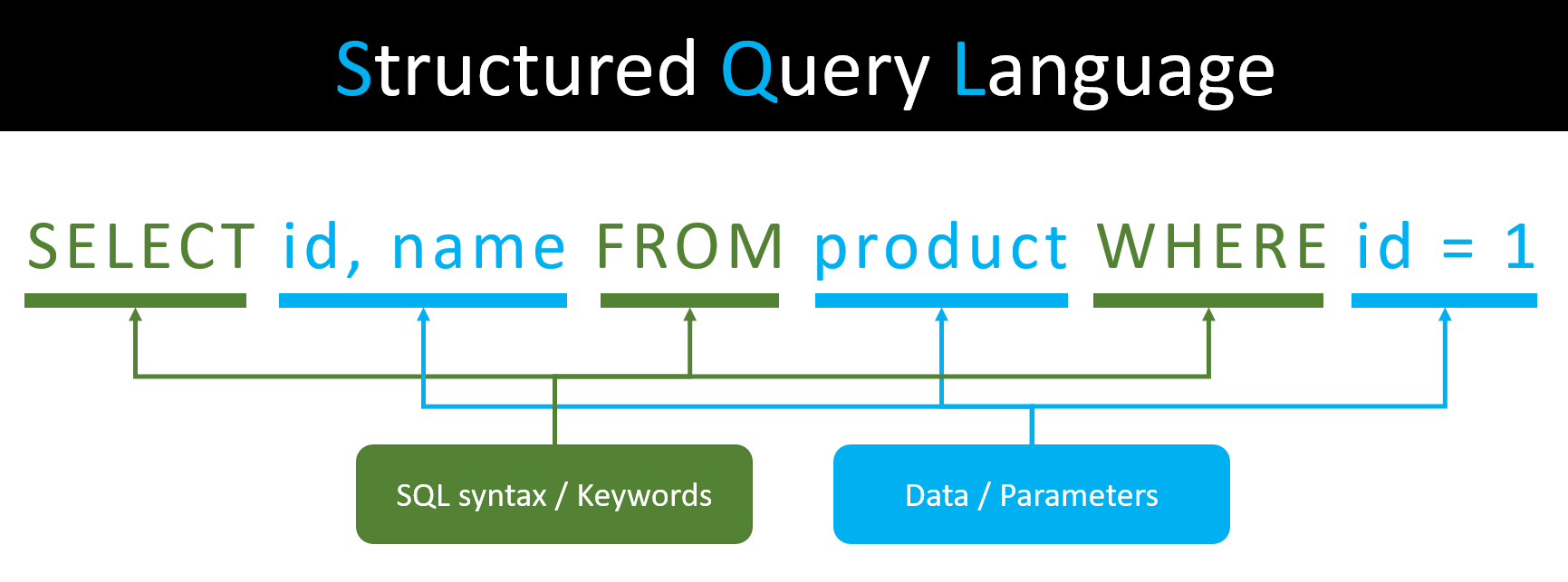
- SQL(Structured Query Language) 관계형 데이터베이스(RDBMS) 또는 SQL 데이터베이스 작업을 위한 표준 언어이다.
- SQL을 사용하여 데이터베이스 객체를 만들고 데이터베이스 레코드를 삽입(INSERT), 업데이트(UPDATE), 삭제(DELETE) 또는 쿼리를 조회(SELECT)할 수 있다.
- SQL은 데이터베이스 최적화 및 유지 관리 또는 데이터 분석 수행과 같은 복잡한 작업에 사용될 수 있다.
- SQL 데이터베이스에는 MySQL, Sybase, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle 등이 많이 사용되고 있다.
-- Query 사용예
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEES (Name, Age, PhoneNumber)
VALUES (“EMP1”, 21, “1234567890”);
데이터베이스 구조(DB Structure)
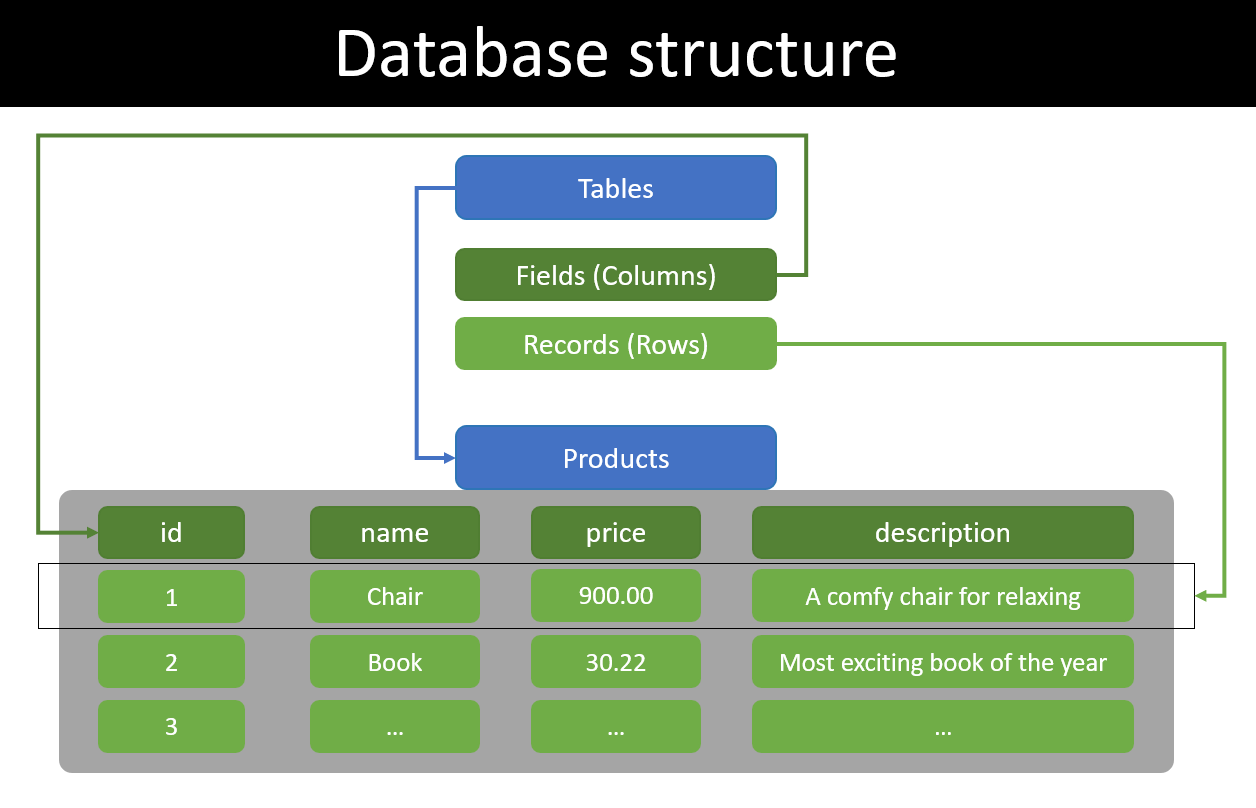
- SQL 데이터베이스 구조의 데이터는 열(row)과 행(column)으로 구성된 테이블로 구성되어 있다.
- SQL 데이터베이스는 수직적 구조로 새로운 데이터가 추가될 때마다 수직적으로 쌓이게 된다.
관계형 데이터베이스(Relational database)
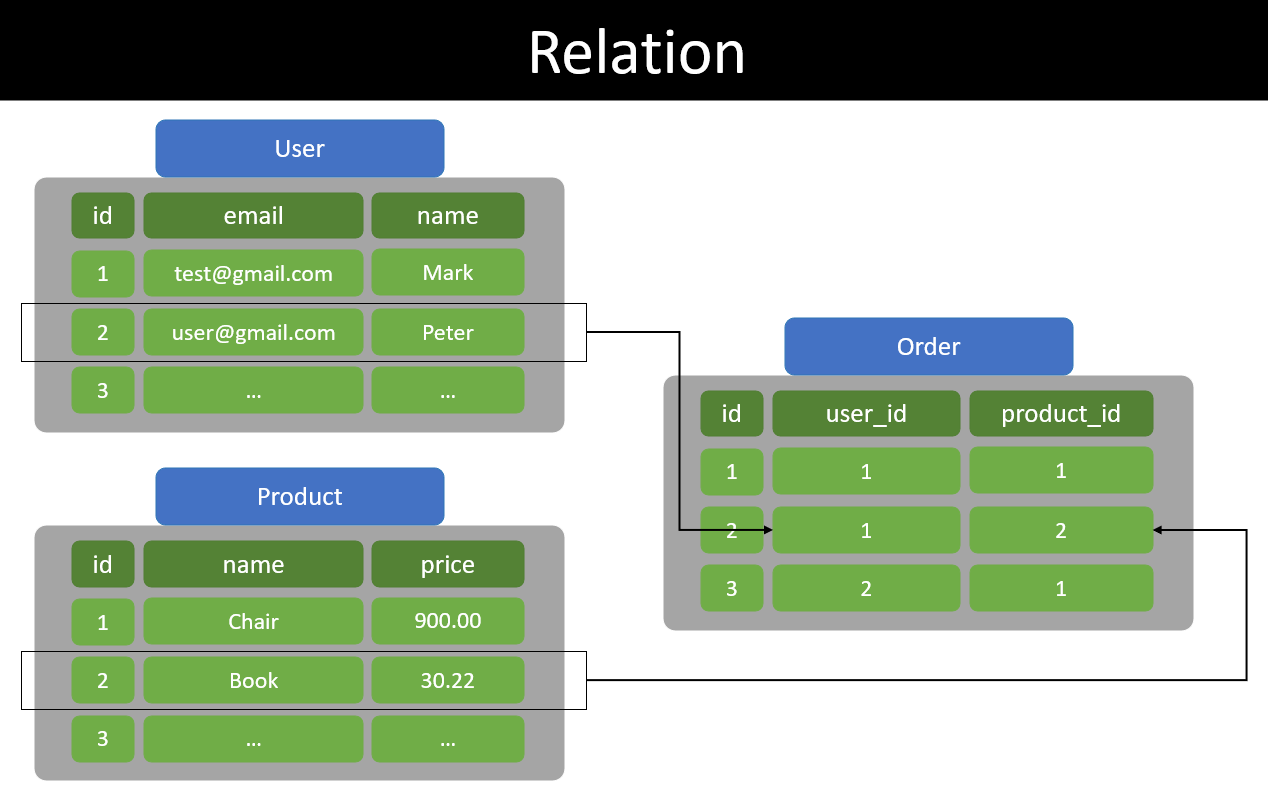
- 관계형 DB(RDBMS)는 데이터베이스에 저장된 데이터의 구조, 즉 데이터 스키마를 명확하게 정의하는 것 또한 매우 중요하다.
- 테이블의 모든 레코드(column - fields)는 정의된 열(row)을 준수해야 하며, 해당 형식(테이블/행/열)에서만 데이터 조작을 수행할 수 있다.
NoSQL(Non SQL) 이란?
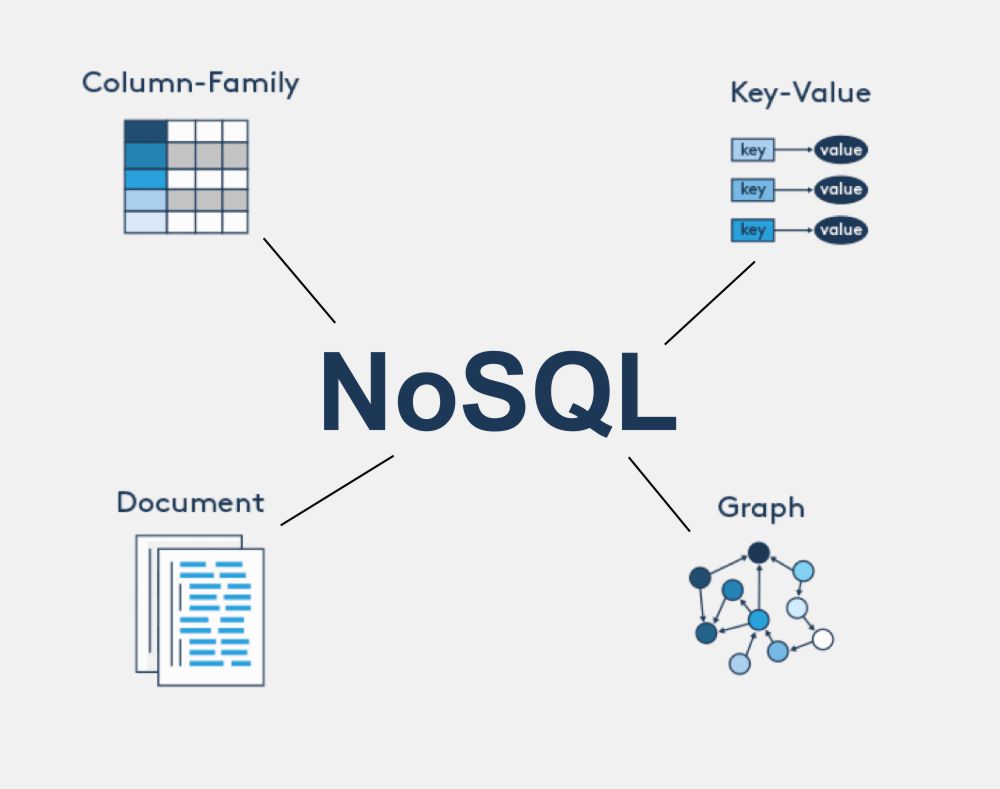
- NoSQL은 고정 스키마가 필요하지 않고 쉽게 확장되며 조인을 수행할 수 없는 비관계형 데이터베이스이다.
- 방대한 데이터 스토리지가 필요한 분산 데이터 저장소에 적합하여 빅데이터와 실시간 웹 앱에 많이 사용된다.
- NoSQL 데이터베이스는 관계형 스키마에 데이터를 저장하지 않기 때문에 전체 테이블의 구조를 변경하거나 나머지 행에 중복 요소를 추가하지 않고도 즉시 데이터 속성을 추가할 수 있다.
- NoSQL 데이터베이스는 수평적 확장이 뛰어나고 파티션 허용 오차가 기반에 내장되어 있어 많은 양의 데이터에 대해 1초 미만의 응답 시간이 필요한 시나리오에서 잘 작동한다.
NoSQL의 종류
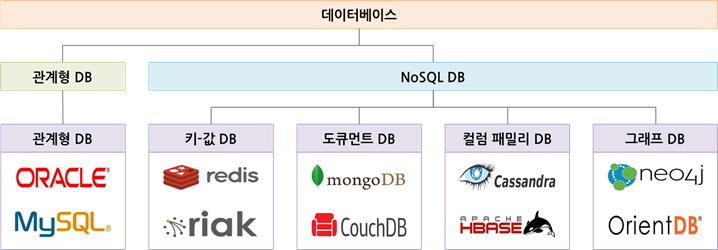
- NoSQL 데이터베이스는 수평적 구조로 새로운 데이터가 추가될 때마다 수평적으로 쌓이게 된다.
Document Databases
[
{
"title" : "The Thieves",
"year" : 2012,
"info" : {
"directors" : [ "Choi Dong-hoon"],
"release_date" : "2012-07-25T00:00:00Z",
"rating" : 8,
"genres" : ["Action", "Drama"],
"image_url" : "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Thieves#/media/File:The_Thieves.jpg",
"plot" : "Ten Thieves. Only One Diamond. They began to Move.",
"actors" : ["Kim Yoon-seok", "Kim Hye-soo", "Lee Jung-jae", "Jun Ji-hyun", "Simon Yam", "Kim Hae-sook", "Oh Dal-su", "Kim Soo-hyun", "Derek Tsang", "Angelica Lee", "Shin Ha-kyun"]
}
},
{
"title": "The Age of Shadows",
"year": 2016,
"info": {
"plot": "Enemy or Comrade",
"rating": 43
}
}
]
- Document DB는 데이터를 JSON 형식의 문서로 데이터를 저장 및 쿼리하도록 설계된 비관계형 데이터베이스이다.
- Document DB를 사용하면 개발자들이 자신의 애플리케이션 코드에서 사용하는 것과 동일한 문서 모델 형식을 사용하여 데이터베이스에서 보다 손쉽게 데이터를 저장하고 쿼리 작업을 할 수 있다.
- Document DB는 문서 및 문서 데이터베이스의 유연하고 반구조화된 계층적 특성을 통해 개발자는 계속해서 애플리케이션의 요구를 발전시킬 수 있다.
- Document DB는 유연한 인덱싱, 강력한 임시 쿼리, 문서 모음에 대한 분석을 지원한다.
- Document DB는 MongoDB, CouchDB, MarkLogic 등이 있다.
// mongo DB Query 사용예
db.movies.insert(
{
"title" : "The Thieves",
"year" : 2012,
"info" : {
"directors" : [ "Choi Dong-hoon"],
// ...
},
},
// ...
)
Key-Value-Based Databases
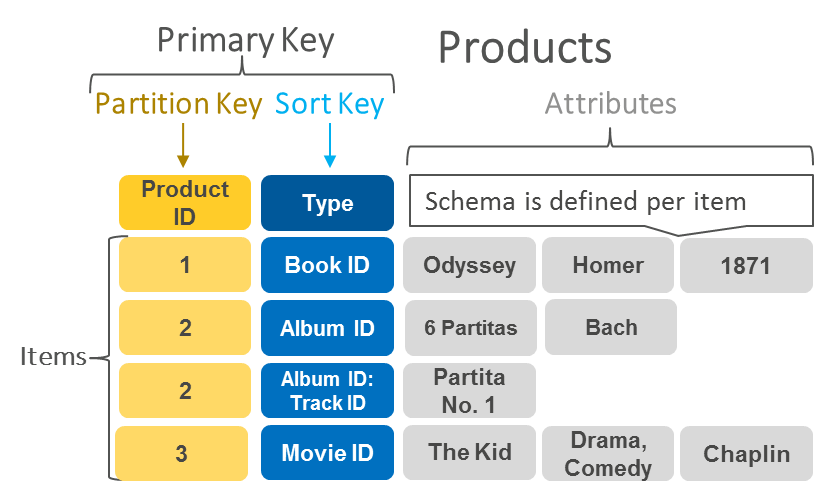
- Key-Value DB는 키-값 메소드를 사용하여 데이터를 저장하는 비관계형 데이터베이스 유형이다.
- Key-Value DB는 key를 고유한 식별자로 사용하는 키-값 쌍의 집합으로 데이터를 저장한다.
- Key-Value DB는 단순한 객체에서 복잡한 집합체에 이르기까지 무엇이든 키와 값이 될 수 있으며 파티셔닝이 가능하고 다른 유형의 데이터베이스로는 불가능한 범위까지 수평 확장을 가능하게 한다.
- Key-Value 기반 DB는 Redis, Memcache 등이 있다.
DynamoDB의 JAVA API를 활용한 key-value 데이터 CRUD 예제
/**
* Copyright 2010-2019 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
*
* This file is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License").
* You may not use this file except in compliance with the License. A copy of
* the License is located at
*
* http://aws.amazon.com/apache2.0/
*
* This file is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
* CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
* specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
*/
package com.amazonaws.codesamples.document;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.AmazonDynamoDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.DeleteItemOutcome;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.DynamoDB;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.Item;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.Table;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.UpdateItemOutcome;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.spec.DeleteItemSpec;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.spec.UpdateItemSpec;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.utils.NameMap;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.document.utils.ValueMap;
import com.amazonaws.services.dynamodbv2.model.ReturnValue;
public class DocumentAPIItemCRUDExample {
static AmazonDynamoDB client = AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder.standard().build();
static DynamoDB dynamoDB = new DynamoDB(client);
static String tableName = "ProductCatalog";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
createItems();
retrieveItem();
// Perform various updates.
updateMultipleAttributes();
updateAddNewAttribute();
updateExistingAttributeConditionally();
// Delete the item.
deleteItem();
}
private static void createItems() {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable(tableName);
try {
Item item = new Item().withPrimaryKey("Id", 120).withString("Title", "Book 120 Title")
.withString("ISBN", "120-1111111111")
.withStringSet("Authors", new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList("Author12", "Author22")))
.withNumber("Price", 20).withString("Dimensions", "8.5x11.0x.75").withNumber("PageCount", 500)
.withBoolean("InPublication", false).withString("ProductCategory", "Book");
table.putItem(item);
item = new Item().withPrimaryKey("Id", 121).withString("Title", "Book 121 Title")
.withString("ISBN", "121-1111111111")
.withStringSet("Authors", new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList("Author21", "Author 22")))
.withNumber("Price", 20).withString("Dimensions", "8.5x11.0x.75").withNumber("PageCount", 500)
.withBoolean("InPublication", true).withString("ProductCategory", "Book");
table.putItem(item);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Create items failed.");
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void retrieveItem() {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable(tableName);
try {
Item item = table.getItem("Id", 120, "Id, ISBN, Title, Authors", null);
System.out.println("Printing item after retrieving it....");
System.out.println(item.toJSONPretty());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("GetItem failed.");
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void updateAddNewAttribute() {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable(tableName);
try {
UpdateItemSpec updateItemSpec = new UpdateItemSpec().withPrimaryKey("Id", 121)
.withUpdateExpression("set #na = :val1").withNameMap(new NameMap().with("#na", "NewAttribute"))
.withValueMap(new ValueMap().withString(":val1", "Some value")).withReturnValues(ReturnValue.ALL_NEW);
UpdateItemOutcome outcome = table.updateItem(updateItemSpec);
// Check the response.
System.out.println("Printing item after adding new attribute...");
System.out.println(outcome.getItem().toJSONPretty());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Failed to add new attribute in " + tableName);
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void updateMultipleAttributes() {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable(tableName);
try {
UpdateItemSpec updateItemSpec = new UpdateItemSpec().withPrimaryKey("Id", 120)
.withUpdateExpression("add #a :val1 set #na=:val2")
.withNameMap(new NameMap().with("#a", "Authors").with("#na", "NewAttribute"))
.withValueMap(
new ValueMap().withStringSet(":val1", "Author YY", "Author ZZ").withString(":val2", "someValue"))
.withReturnValues(ReturnValue.ALL_NEW);
UpdateItemOutcome outcome = table.updateItem(updateItemSpec);
// Check the response.
System.out.println("Printing item after multiple attribute update...");
System.out.println(outcome.getItem().toJSONPretty());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Failed to update multiple attributes in " + tableName);
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void updateExistingAttributeConditionally() {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable(tableName);
try {
// Specify the desired price (25.00) and also the condition (price =
// 20.00)
UpdateItemSpec updateItemSpec = new UpdateItemSpec().withPrimaryKey("Id", 120)
.withReturnValues(ReturnValue.ALL_NEW).withUpdateExpression("set #p = :val1")
.withConditionExpression("#p = :val2").withNameMap(new NameMap().with("#p", "Price"))
.withValueMap(new ValueMap().withNumber(":val1", 25).withNumber(":val2", 20));
UpdateItemOutcome outcome = table.updateItem(updateItemSpec);
// Check the response.
System.out.println("Printing item after conditional update to new attribute...");
System.out.println(outcome.getItem().toJSONPretty());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error updating item in " + tableName);
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void deleteItem() {
Table table = dynamoDB.getTable(tableName);
try {
DeleteItemSpec deleteItemSpec = new DeleteItemSpec().withPrimaryKey("Id", 120)
.withConditionExpression("#ip = :val").withNameMap(new NameMap().with("#ip", "InPublication"))
.withValueMap(new ValueMap().withBoolean(":val", false)).withReturnValues(ReturnValue.ALL_OLD);
DeleteItemOutcome outcome = table.deleteItem(deleteItemSpec);
// Check the response.
System.out.println("Printing item that was deleted...");
System.out.println(outcome.getItem().toJSONPretty());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error deleting item in " + tableName);
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Column-Oriented/Family Databases
1.Column-Oriented Databases
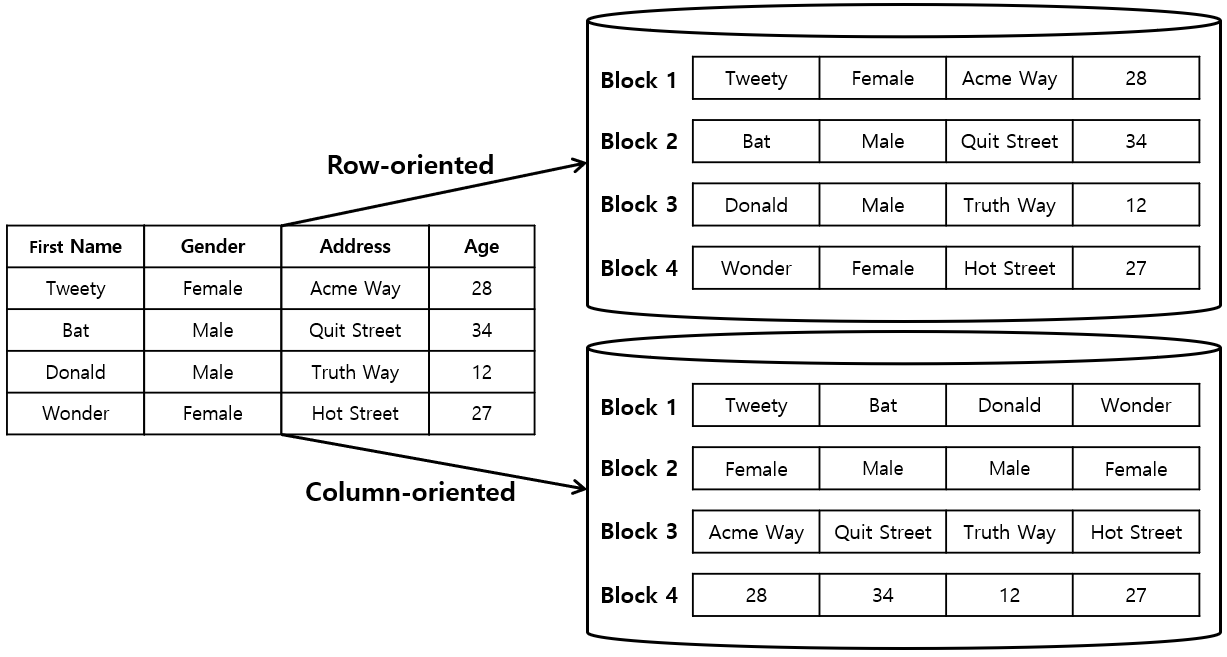
- Column-Oriented DB는 Tabled의 data를 Column 단위로 쪼개어 저장하는 DB를 의미한다.
- Column-Oriented DB는 하나의 Column이 하나의 Disk Block안에 저장된다.
- Column-Oriented DB는 1개의 Block만 읽고 결과를 구할 수 있기 때문에 빠른 처리가 가능하다.
- 이처럼 Data를 분석하는 동작의 경우 Data Table에서 모든 Column이 필요한 것이 아니라 일부 Column이 필요한 경우가 대부분이다.
- 따라서 Column-oriented DB는 OLAP(Online Analytical Processing) 처리에 유리한 반면, OTLP(Online transaction processing) 처리에 불리하다.
2.Column-Family Databases
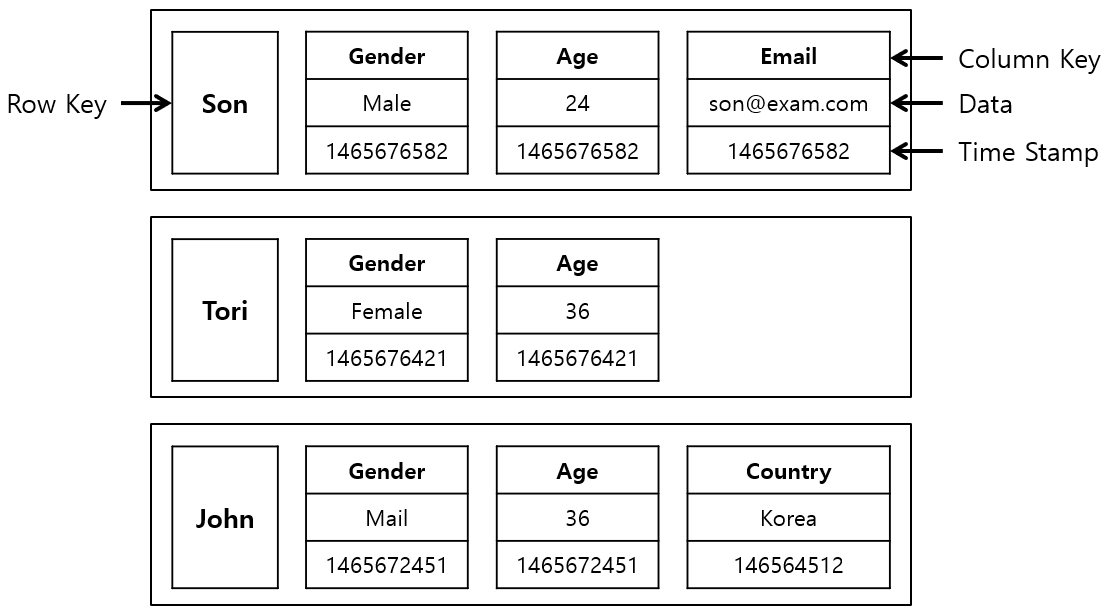
- Column-Family DB는 Column을 나타내는 Column Key/Data/Timestamp Tuple을 Row를 나타내는 Row Key에 Mapping하여 Data Table을 표현하는 DB이다.
- RDBMS에서 NULL값도 Disk Block 공간을 차지하지만 Column Family DB에서는 Row별로 자유로운 Column 추가/삭제가 가능하기 때문에 NULL값을 위한 Column이 별도로 필요없다.
- 일반적으로 Column-oriented DB와 Column Family DB가 혼용되어 사용되어 Column Family DB가 Column-oriented DB라고 간주하는 경우가 많은데 같은 DB라고 할 수는 없다.
- Column Family DB인 HBASE는 Column의 집합인 Column Family 단위로 Disk Block에 저장되기 때문에 Column-oriented DB로 분류된다.
- 하지만 또 하나의 Column Family DB인 Cassandra는 Row 단위로 Disk Block에 저장되기 때문에 Column-oriented DB라고 할 수 없다.
Cassandra DB의 CRUD 예제
-- create a tuple
CREATE TABLE subjects (
k int PRIMARY KEY,
v tuple<int, text, float>
);
-- insert values
INSERT INTO subjects (k, v) VALUES(0, (3, 'cs', 2.1));
-- retrieve values
SELECT * FROM subjects;
Graph Databases
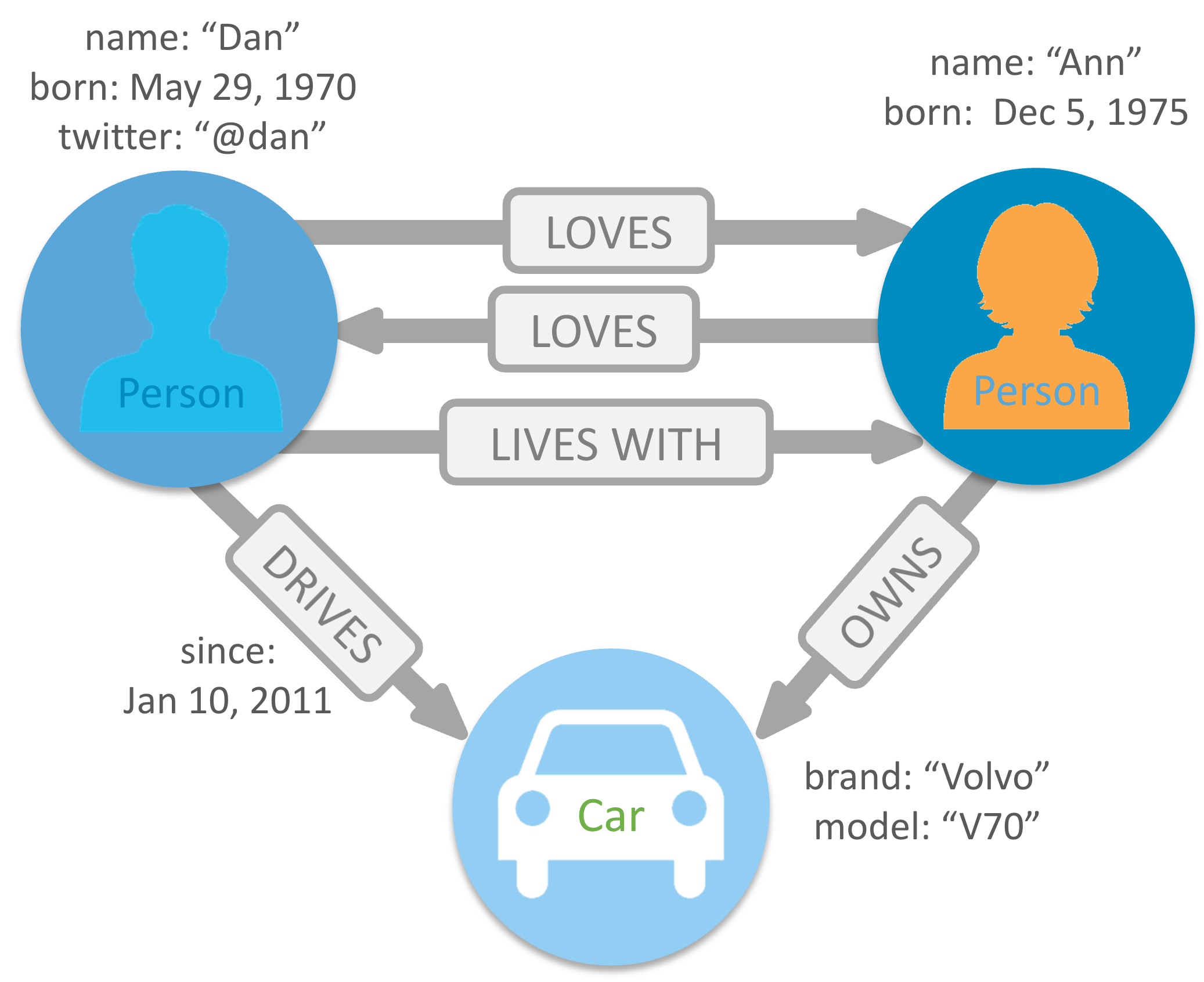
- Graph DB는 관계를 저장하고 탐색하도록 특별히 구축되다.
- Graph DB는 노드를 사용하여 데이터 엔터티를 저장하고, 엣지로는 엔터티 간의 관계를 저장하게 되는데, 엣지는 항상 시작 노드, 끝 노드, 유형과 방향을 가지며, 상-하위 관계, 동작, 소유자 등을 문서화 한다.
- 하나의 노드가 가질 수 있는 관계의 수와 종류에는 제한이 없다.
- Graph DB 그래프는 특정 엣지의 유형 또는 전체 그래프를 전반을 통하여 트래버스될 수 있다.
- Graph DB에서 노드 간의 관계는 쿼리 시간에는 포함되지 않지만 데이터베이스에서 유지되기 때문에 조인 또는 관계를 트래버스하는 속도가 매우 빠르다.
- Graph DB는 데이터 간의 관계를 만들고 이러한 관계를 신속하게 쿼리해야 할 때 소셜 네트워킹, 추천 엔진, 이상 탐지 등의 사용 사례에 유용하다.
- Graph DB는 Neo4j, RedisGraph(Redis에 내장된 그래프 모듈), OrientDB 등이 있다.
Neo4j DB의 예제
MATCH (tom:Person {name:"Tom Hanks"})-[:ACTED_IN]->(m)<-[:ACTED_IN]-(coActors)
RETURN tom, m, coActors
결론!
SQL과 NoSQL 비교
| Parameter | SQL | NoSQL |
|---|---|---|
| 관계 | 관계형 | 비관계형 |
| 쿼리 언어 | 구조화된 쿼리 언어(SQL) | 문서, 키-값, 그래프, 컬럼기반 |
| 사용 | OLAP 시스템에 사용 | 최신 애플리케이션 개발에 대한 요구에 부응하여 개발 |
| 개요 | 미리 정의된 스키마 | 구조화되지 않은 데이터에 동적 데이터베이스를 사용 |
| 확장성 | 수직 확장 | 수평 확장 |
| 유형 | 테이블 기반의 DB | 문서 기반, 키-값 쌍 또는 그래프 DB |
| 계층적 데이터 저장 | 적합하지 않음 | 적합 |
| 대표적인 DB | SQL, MySQL, MS-SQL, Postgres | MongoDB, Redis, Neo4j, Cassandra, Hbase |
2022 DB Ranking
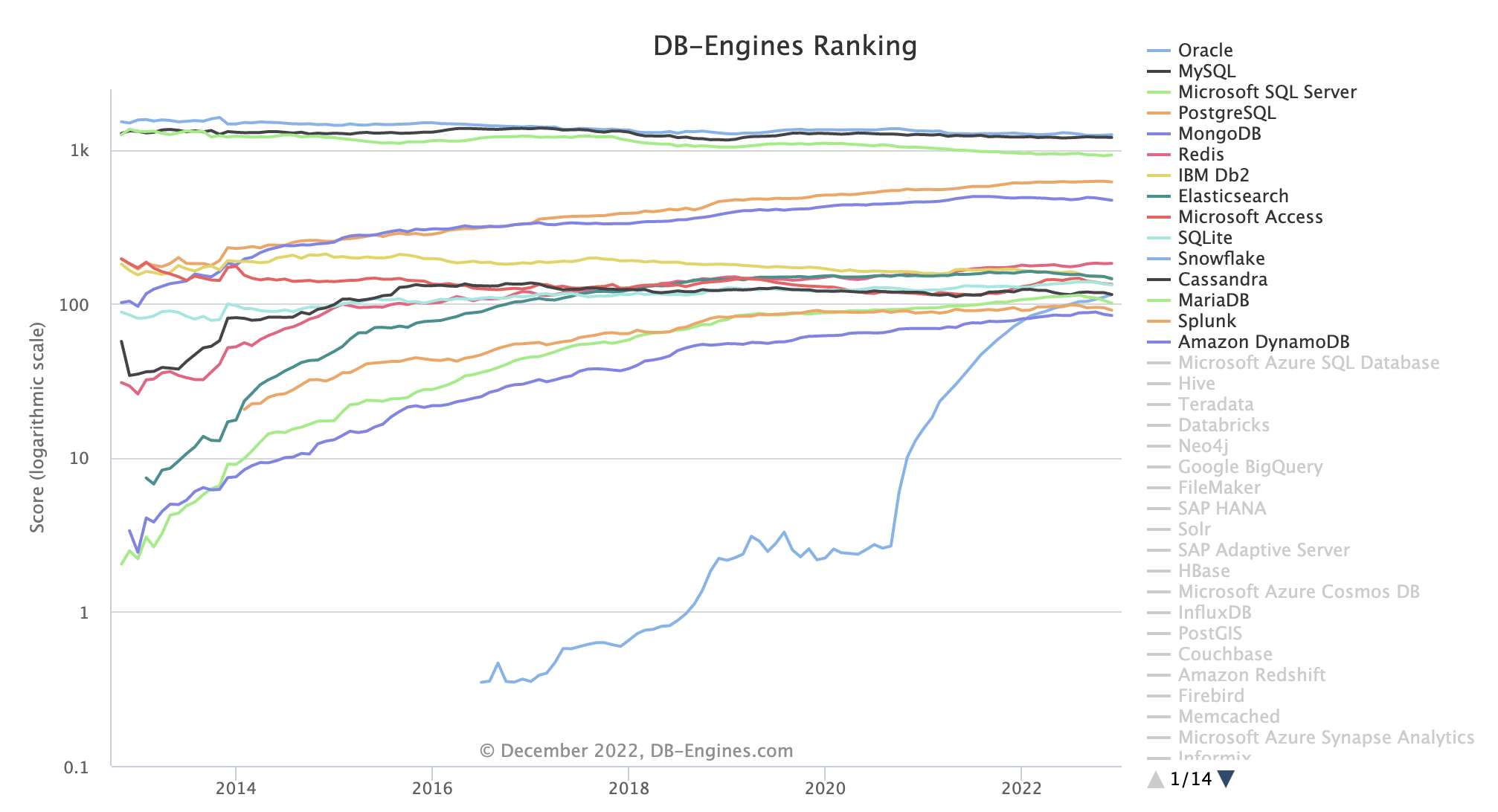
- SQL의 언어의 사용량이 높긴 하지만 NoSQL의 사용량도 점차 꾸준히 늘고 있다. 즉, 기획하고 설계하는 프로젝트에 대해 선택하는 언어가 다른 거 같다. 어느 한쪽이 좋은 언어 라고 얘기하기는 어려운 거 같다. 각자의 장/단점이 있는 언어이기 때문에 해당 프로젝트에 가장 알맞은 언어를 선택하여 설계하여 개발하는 것이 가장 좋은 거 같다.
